
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
Infrared communication, as its name suggests, transmits data via infrared. In the early days of computer technology development, data was transmitted through cables. Cable transmission lines were troublesome and required special interfaces, which was quite inconvenient. Then there were wireless data transmission technologies such as infrared, Bluetooth, and 802.11. In the early days of infrared communication technology development, there were several infrared communication standards, and infrared devices between different standards could not perform infrared communication. In order to enable various infrared devices to be interconnected, in 1993, the Infrared Data Association (IrDA) was established by more than 20 major manufacturers to unify the standard of infrared communication. This is the widely used IrDA infrared data communication protocol and specification.
What are the advantages of infrared communication compared with wireless communication?Infrared communication uses infrared rays as a carrier to transmit data information. As a kind of wireless communication, compared with radio communication, it can be used for indoor and outdoor point-to-point and wireless because of its high performance-price ratio, simple implementation, anti-electromagnetic interference, high-speed application, flexible space access and economy. Infrared LAN communication and military infrared fuzes have been widely used in mobile computing and mobile communication devices.
In some cases, where data exchange is required but not very large, and the real-time requirements are not very high, infrared communication can be used, so that the convenience brought by the cordless communication can be obtained, and the radio can be avoided. Some problems may arise from high frequency circuits. For example, a remote controller for household appliances, a remote keyboard and a remote mouse for a computer, and a portable data collection device (a register for a coal-water meter, a tax collector) and a host for data exchange.
At present, wireless data communication using infrared rays is highly feasible in terms of miniaturization, light weight, and security, and has been used in wireless multi-channel indoor voice systems, cordless phones, and between keyboards and terminals. It has been applied in short-range wireless connections. The working bandwidth in all of these applications is much lower than the bandwidth required by the WLAN.
Remote infrared communication principleIn the field of actual communication, the transmitted signal generally has a wide spectrum, and all of them distribute a large amount of energy in a relatively low frequency range, so it is called a baseband signal, and this signal is not suitable for transmission directly in the channel. . In order to facilitate transmission, improve anti-interference ability and effectively utilize bandwidth, it is usually necessary to modulate the signal into a frequency range suitable for channel and noise characteristics. This is called signal modulation. At the receiving end of the communication system, the received signal is demodulated to recover the original baseband signal. The content of this part of the communication principle, you can understand.
The infrared communication in the infrared remote control that we usually use is usually modulated by using a carrier of about 38K. Below I will introduce the principle to you. Let's take a look at the principle of sending.
Modulation: It is the process of controlling the amplitude, phase, frequency and other parameters of a high-frequency signal by using the signal to be transmitted, that is, using one signal to load another signal. For example, when our infrared remote control signal is to be transmitted, it is first modulated by 38K, as shown in Figure 1.
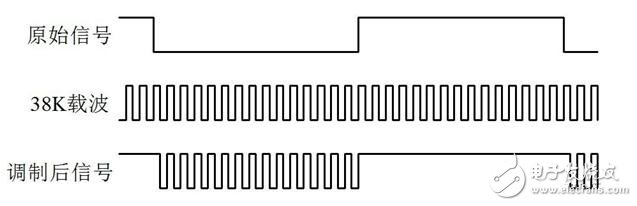
Figure 1 Infrared signal modulation
The original signal is a data "0" bit or a data "1" bit that we want to send, and the so-called 38K carrier is a square wave signal with a frequency of 38K. The modulated signal is the waveform that we finally emit. We use the original signal to control the 38K carrier. When the signal is data "0", the 38K carrier is transmitted without any reservation. When the signal is data "1", no carrier signal is transmitted.
In principle, how do we implement this function from a circuit perspective? as shown in picture 2.

Figure 2 Schematic diagram of infrared emission
For the 38K carrier, we can use the 455K crystal oscillator to get 37.91K after dividing by 12, or it can be generated by the time base circuit NE555, or by using the PWM of the microcontroller. When the signal output pin outputs a high level, Q2 is turned off. No matter how the 38K carrier signal controls Q1, the vertical branch on the right side will not be turned on, and the infrared tube L1 will not send any information. When the signal output is low, then the 38K carrier will be released through Q1, producing a 38K carrier signal on L1. It should be noted that the 38K duty cycle of most home appliance remote controllers is 1/3, and there are also 1/2, but relatively few.
For normal communication, the receiver must first process the signal through a series of circuits such as monitoring, amplification, filtering, demodulation, etc., and then output the baseband signal. However, the integrated receiving head HS0038B of infrared communication has integrated all of these circuits together. We only need to connect this circuit to directly output the baseband signal we want, as shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3 infrared receiving schematic
Since the gain of the internal amplifier of the infrared receiving head is very large, it is easy to cause interference. Therefore, the filter capacitor must be added to the power supply pin of the receiving head. The value given by the official manual is 4.7uF. The 10uF used directly here is also required in the manual. A 100 ohm resistor is placed in series between the supply pin and the power supply to further reduce interference.
The circuit shown in Figure 3 is used to receive the waveform sent by the circuit of Figure 16-5. When HS0038 detects that there is a 38K infrared signal, it will output a low level on the OUT pin. When there is no 38K, OUT leads. The foot will output a high level. Then we connect the OUT pin to the IO port of the microcontroller, and through programming, we can get the data sent by the infrared communication.
Think about it, is the data output from the OUT pin restored to baseband signal data? Then, when we receive this baseband signal data, how do we judge what data is received, what protocol should we follow? Communication protocols such as UART, I2C, and SPI that we learned before are the communication protocols for baseband communication, while the infrared 38K only modulates and demodulates the baseband signal, making the signal more suitable for transmission in the signal.
Since our infrared modulation signal is half-duplex and only one source is allowed in the space, our infrared baseband signal is not suitable for I2C or SPI communication protocol. We mentioned that UART is 2 Line, but when communicating, actually one line is OK, so the infrared can communicate in the UART. Of course, this communication is not unlimited. For example, in the data sheet of HS0038B, if the HS0038B is to recognize the 38K infrared signal, then the 38K carrier must be greater than 10 cycles, which limits our infrared communication. The bit rate of the baseband signal must not be higher than 3800. If the signal output from the serial port is directly modulated by 38K, the baud rate cannot be higher than 3800.
Common infrared remote control protocolI. NEC Agreement
feature:
8-bit address and 8-bit command length for improved reliability. Two-pass address (user code) and command (key value) for each transmission. The modulation of the signal is achieved by the time interval between the bursts. The 38Khz carrier has a period of 1.12ms per bit. Or 2.25ms
Modulation:

Note: For the signal of the infrared receiver, the place where the pulse signal is high is high. That is, the logic "1" is 0.56ms high level + 1.69ms low level, and the logic "0" is 0.56ms high level +0.56ms low level.
protocol:

The figure above shows a typical NEC protocol transmission format. The start bit (boot code) is 9ms high + 4.5ms low. The valid data is address + address inverse code + command + command inverse code. The purpose of the inverse is to calibrate the previous address and command. If you are not interested in reliability, you can also remove the inverted data or extend the address and command to 16 bits.
The address data transmitted in the above figure is 10011010. It should be noted that the low-order address is sent first and then the high-order address is sent. Therefore, the address of the waveform is 01011001=0X59. Similarly, the command is 00010110=0X16.
When the button is pressed, as shown in the figure below, it is sent once every 110ms, but the command is sent only once. The repeat is 9ms high + 2.25ms low + 0.56ms high + low

Extended protocol:

The extension protocol simply changed the address to 16 bits, the others unchanged.
Measured waveform:
The waveform below is the waveform obtained from the infrared receiver: (the modulated pulse signal is converted to high and low levels)

Since the infrared receiving head reverses the waveform when receiving the signal (or when transmitting), the reverse function of the oscilloscope can be turned on while reading the data, and the valid data can be read.
The following example is the waveform captured by the known NEC type remote control:
The remote control ID is Address=0xDD20; one of the key values is Command=0x0E

The last bit is a logical "1".
Second, Philips RC5 agreement
feature:
5-bit address and 6-bit command length (7-bit extension protocol)
Bidirectional encoding or Manchester encoding (ie, level changes to represent logic 0 and 1)
36Khz carrier
The period per bit is 1.778ms (64 cycles of 36 kHz)
Modulation:


protocol:

A piece of data consists of 14 bits with a period length of 25ms.
The first two bits are the start bit S which is usually a logic one.
In RC5 extended mode, the second bit S2 expands the 6-bit command code to the 7-bit code (as the MSB), which can be expanded from 64 key values to 128 key values.
The third bit is the control bit C. It flips after each key is pressed, so that it can be distinguished whether a key is pressed repeatedly without releasing the hand or releasing it.
When the button is pressed, the data is sent repeatedly every 114ms, and the third bit does not flip, that is, the signals sent repeatedly are completely consistent.
Measured waveform:
When the same button is pressed twice in succession, only the third bit is flipped, and the other bits are unchanged.

The value of the segment data can be read from the above waveform as 101 01010 010111. Since the protocol is the RC5 extension protocol, that is, the second bit is the seventh bit of the command, the address is 01010=0X0A, and the command is 0010111=0X17. (The actual remote controller manufacturer gives a command of 57, which may be the seventh bit of the command after inverting the second bit).
Third, the Sony SIRC agreement
feature:
There are three modes of 12, 15, and 20 digits (12-bit mode described below)
5-bit address and 7-bit command length
Pulse width coding
40Khz carrier
The period of each bit is 1.2ms or 1.8ms
Modulation:

protocol:

The start bit is 2.4ms high level +0.6ms low level;
When the button is pressed, the data is sent repeatedly every 45ms.
Measured waveform:

From the above waveform, the value of the segment data can be read as 1001000 10000 cmd:0001001 addr: 00001.
Fourth, other
1, ITT

2, JVC

3, Nokia NRC17

4, RCA

5, Sharp

6, X-Sat

January 10, 2024
Mail a questo fornitore

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.